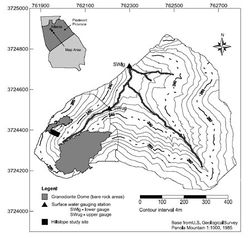
Panola Mountain Research Watershed
Location
The Panola Mountain Research Watershed (PMRW) is located within the Panola Mountain State Conservation Park, about 25 km southeast of Atlanta, Georgia, USA (84°10’W, 33°37’N).
Catchment size
- 41 ha main catchment
- 10 ha sub-catchment located in the western part of the catchment
- 0.1 ha trenched hillslope
Climate
Humid continental to subtropical.
The mean annual precipitation is ~1240 mm, which on average is distributed uniformly throughout the year. Rainfall typically has a long duration and low intensity associated with the passage of fronts in the winter and has a short duration and high intensity associated with convective rainstorms in the summer.
Geology
The bedrock is predominantly the Panola Granite (granodiorite composition), a biotite–oligioclase– quartz–microcline granite of Mississippian to Pennsylvanian age. The Panola granite contains pods of amphibolitic gneiss, particularly at lower elevation.
Soils are predominantly ultisols developed in colluvium and residuum, which intergrades to inceptisols developed in colluvium, recent alluvium, or in highly eroded landscape positions. Typical soil profiles on the hillslopes are 0.6 to 1.6 m thick, grading into saprolite of variable thickness. The riparian zone has the deepest soils (>5 m).
Topography
The basin relief is 56 m and slopes average 18%.
Vegetation/Land use
The watershed contains a naturally regenerated second-growth forest on abandoned agricultural land, typical of the Piedmont physiographic province. The watershed is 90% forested, dominated by hickory, oak, tulip poplar, and loblolly pine, and 10% partially vegetated (lichens and mosses) bedrock outcrops. The forested area varies from 100% deciduous to 100% coniferous.
Context of investigation
The PMRW was established in 1985 as part of the USGS Acid Rain Thrust Program. In 1991, the 41-ha forested watershed became one of five Water, Energy and Biogeochemical Budgets (WEBB) sites focusing research on the movement of water and solutes within a small forested watershed and the effects of anthropogenic and environmental change. The experimental hillslope study site was established in 1995 with the excavation of a 20-m-long trench.
Measurements/Equipment
41 ha main catchment and 10 ha subcatchment:
- Precipitation
- Climate
- Streamflow at the catchment outlet and the 10 ha sub-catchment
- Several transects with recording wells
- Water quality (weekly and event sampling)
- Soil moisture
0.1 ha hillslope study site:
- Lateral subsurface flow (trench)
- Soil moisture
- Groundwater
- Sapflow (Summer of 2002)
- Sprinkling experiments (Summer of 2002 and Fall of 2006)
- Tracer experiments (Summer of 2002 and Fall of 2006)
Links to project webpages
http://ga.water.usgs.gov/projects/panola/