Difference between revisions of "Forest Floor Interception"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
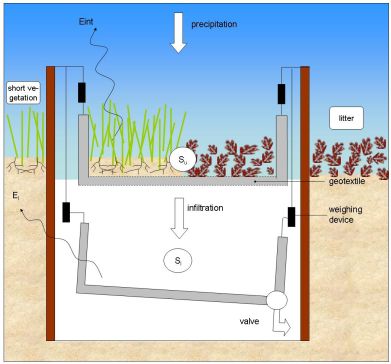
''Figure 1: Schematic drawing of the interception device with Eint the evaporation from interception, El the evaporation from the lower basin and Su and Sl the storage in respectively the upper and lower basin.'' | ''Figure 1: Schematic drawing of the interception device with Eint the evaporation from interception, El the evaporation from the lower basin and Su and Sl the storage in respectively the upper and lower basin.'' | ||
| − | To calculate the amount of evaporation from interception, a water balance is made of the system. When evaporation from the lower basin (El [L T−1]) is neglected and the weight of the lower basin is corrected for the drainage from the valve (Sl [L]), evaporation of intercepted rainfall | + | To calculate the amount of evaporation from interception, a water balance is made of the system. When evaporation from the lower basin (El [L T−1]) is neglected and the weight of the lower basin is corrected for the drainage from the valve (Sl [L]), evaporation of intercepted rainfall Eint [L T−1]) can be calculated as: |
| − | <math> | + | <math>E_int(t)=P_{net}(t)-\left \frac{dS_{u}}{dt}+\frac{dS_{l}}{dt}\right <math> |
where Su and Sl are respectively the storage of the upper and the lower basins [L], which are obtained by dividing the weight of the basins [M] by the density of water [M L−3] and the surface area [L2] of the basin. | where Su and Sl are respectively the storage of the upper and the lower basins [L], which are obtained by dividing the weight of the basins [M] by the density of water [M L−3] and the surface area [L2] of the basin. | ||
Revision as of 13:17, 8 March 2007
To measure evaporation from intercepted rainfall on the forest floor, a special device has been developed. The device consists of two aluminium basins, which are mounted above each other and are weighed accurately with 2 sets of 3 strain gauge sensors (see Figure 1). One sensor consists of a metal ring where four strain gauges are mounted in the Wheatstone configuration. The upper basin is filled with forest floor and has a permeable bottom of geotextile, so water can percolate into the lower basin. A valve is installed in this lower basin, which empties every day for 10 min to avoid evaporation from the lower basin as much as possible. The space between the supporting structure and the aluminium basins is also minimized, in order to avoid evaporation by turbulent wind fluxes. In addition to the weight, the temperature is also measured in one of the lower strain gauge casings and saved on a data logger every minute.
Figure 1: Schematic drawing of the interception device with Eint the evaporation from interception, El the evaporation from the lower basin and Su and Sl the storage in respectively the upper and lower basin.
To calculate the amount of evaporation from interception, a water balance is made of the system. When evaporation from the lower basin (El [L T−1]) is neglected and the weight of the lower basin is corrected for the drainage from the valve (Sl [L]), evaporation of intercepted rainfall Eint [L T−1]) can be calculated as:
<math>E_int(t)=P_{net}(t)-\left \frac{dS_{u}}{dt}+\frac{dS_{l}}{dt}\right <math>
where Su and Sl are respectively the storage of the upper and the lower basins [L], which are obtained by dividing the weight of the basins [M] by the density of water [M L−3] and the surface area [L2] of the basin.
Figure 2: Interception device in the Huewelerbach catchment (Luxembourg) on January 2006. The upper basin is filled with leaf litter.
THIS ARTICLE CAME FROM: Gerrits, A.M.J., Savenije, H.H.G., Hoffmann, L. and Pfister, L. (2007): New technique to measure forest floor interception – an application in a beech forest in Luxembourg, Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 11, 695-701.